In the ever-evolving digital technology environment, blockchain has become a revolutionary force with the potential to transform various industries. At the heart of this decentralized technology is a critical component known as nodes, which play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity, security, and resilience of the blockchain network.
Although the concept of blockchain often makes headlines, it is the nodes that silently act as gatekeepers, ensuring the smooth operation of this groundbreaking technology. Nodes serve as the backbone of the blockchain, promoting trust, transparency, and consensus among network participants without relying on a central authority.
In this article, we will delve into the world of nodes and explore their significance in the blockchain ecosystem. We will unravel the multifaceted roles they play, shedding light on how they contribute to the decentralized nature of blockchain networks and fortify the trustworthiness of transactions.
Furthermore, we will examine the various types of nodes, their functionalities, and the responsibilities they shoulder in maintaining the blockchain’s integrity.
What is a node?
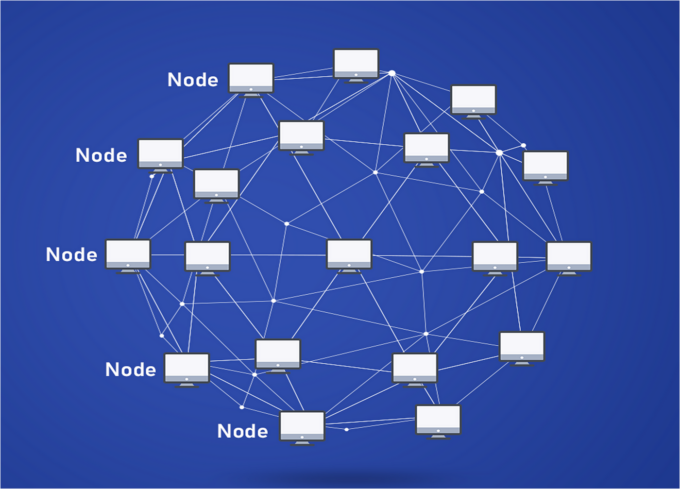
Nodes are called servers with special software. It can be a computer or other computing equipment that is connected to the cryptocurrency blockchain network.
There are several types of such servers. Each individual of them stores the history of the blockchain in full or in another version, sufficient to perform the functions of this element of the network. Nodes interact with each other using P2P protocols.
What are nodes for?
Nodes monitor the reliability of information in the blockchain. They verify and confirm transactions and new blocks, thereby ensuring the security of the cryptocurrency network.
The blockchain stores information about all transactions that have ever been carried out on the network since its launch. Miners pack data on operations with cryptocurrency into blocks from which a continuous chain is formed. Each subsequent block includes an encrypted “concentrate” of information from the previous block to link the elements of the chain to each other.
If at least one character is changed in an already existing block, the link will be broken. That is, removing, adding or changing the record of transferring coins to an exchange service to convert BNB to BTC or any other crypto pair is technically possible, but not feasible in practice. Nodes stand guard over the integrity of the blockchain and constantly check the information in the blockchain with other nodes.
What are the nodes?

Full: On such a server, the entire history of the blockchain is stored, and their owners have maximum authority to participate in network management. Any decisions to improve the project are made by voting. Sometimes it is not possible to reach an agreement and in such cases it is possible to initiate a hard fork of the chain. The more full nodes in the network, the higher its security, because the more participants, the more difficult it is for them to collude to distort information or falsify the vote.
Lightweight: Unlike a complete download of the entire blockchain, it is not required to start the server, only the block headers are enough. Lightweight nodes cannot function without full nodes, from which they receive the missing information about the state of the blockchain. Suppose it is possible to find information about XSR exchange rate changes outside the blockchain, and in order to study the early blocks of this network, you will inevitably have to interact with other network controls
Trimmed full: The server only maintains the latest transactions, according to the specified storage settings. old blocks are “trimmed” by the system to save memory.
Mining: They serve to confirm transactions for the creation of new blocks. Their owners are rewarded for their care.
Authority nodes: Although cryptocurrencies were created as decentralized systems, some blockchains still have elements of centralization. The owners of such networks appoint transaction validators, but otherwise technically such a server works in the same way as a full node. There is at least one more rather exotic kind of network elements of this type – supernodes that operate in the NEM cryptocurrency network.
Masternode: Such nodes are also technically very similar to full ones. They are needed to check and record information about transactions, but they cannot add blocks to the network. Their masternode owners are rewarded for their work in native network tokens. As a rule, the launch requires a deposit in the network’s native tokens, and these can be quite large amounts. The process itself can be regarded as the organization of passive mining.
Lightning node: Designed to facilitate off-chain transactions, connect users inside and outside of the main blockchain.

Running some types of nodes on your own equipment can be a good option for passive income from cryptocurrency. Theoretically, any user who has a computing device and a stable, uninterrupted Internet connection can do this. In practice, to organize the work of verifying transactions in some networks, quite large initial investments will be required.
In this article, we have explored the fundamental importance of nodes in upholding the principles of decentralization, security, and trust in blockchain networks. Their tireless efforts ensure that transactions are verified, consensus is reached, and the integrity of the blockchain is maintained.
As I have seen, nodes come in many forms, each with their own unique responsibilities and contributions. Whether they are full nodes that store the entire history of the blockchain, mining nodes that verify transactions and add blocks to the chain, or light nodes that rely on others for verification, each node serves a vital purpose in the overall functioning of the blockchain ecosystem.
In addition, nodes serve as an important line of defense against potential threats and attacks. Their distributed nature and consensus mechanisms make it extremely difficult for attackers to manipulate the system. By participating in the consensus process, nodes contribute to the reliability and resilience of the blockchain network, making it highly resistant to censorship, fraud, and unauthorized changes.
Looking ahead, we can say that the role of nodes will evolve along with the ever-evolving blockchain technology. With the emergence of new consensus algorithms such as proof-of-stake, nodes are adapting and will continue to play an important role in the consensus and governance of blockchain networks.