Scrum is an agile framework for project management and product development, particularly in the context of software development. It provides a structured and flexible approach to managing complex projects and delivering high-value products. It is based on a set of principles and practices that emphasize collaboration, adaptability, and continuous improvement. Here are the key elements of Scrum:
1. Roles:
- Scrum Master: The Scrum Master is responsible for ensuring that the Scrum framework is understood and applied correctly. They help the team and organization use Scrum effectively, remove impediments, and facilitate events.
- Product Owner: The Product Owner represents the stakeholders and is responsible for defining the product backlog, prioritizing items, and ensuring that the team delivers value to the customers.
- Development Team: The development team is responsible for delivering potentially shippable increments of the product. It is a self-organizing and cross-functional group of individuals.
2. Artifacts:
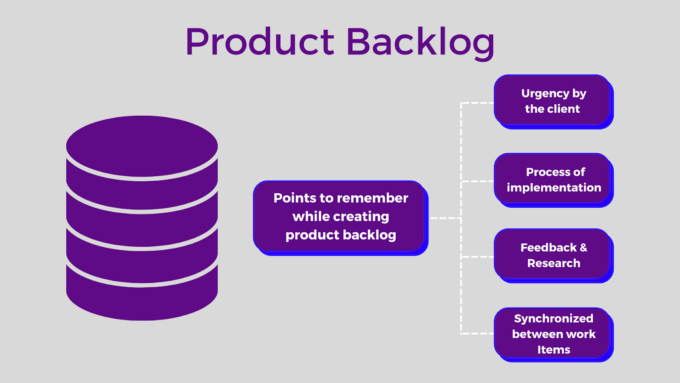
- Product Backlog: This is a prioritized list of all the work that needs to be done on the project. The Product Owner maintains it and constantly refines it.
- Sprint Backlog: For each sprint (a time-boxed period, usually 2-4 weeks), the team selects a set of items from the product backlog to work on during that sprint.
- Increment: At the end of each sprint, the development team delivers a potentially shippable product increment.
3. Events:
- Sprint: A time-boxed period during which the development team works to complete the items selected in the sprint backlog.
- Sprint Planning: A meeting that occurs at the beginning of a sprint where the team selects items from the product backlog for the sprint backlog.
- Daily Stand-Up (Daily Scrum): A daily meeting where team members synchronize their work and discuss progress, plans, and any impediments.
- Sprint Review: Held at the end of each sprint, this meeting is where the team demonstrates the increment to stakeholders and receives feedback.
- Sprint Retrospective: Also held at the end of each sprint, this meeting is a time for the team to reflect on their process and identify ways to improve.
4. Rules:
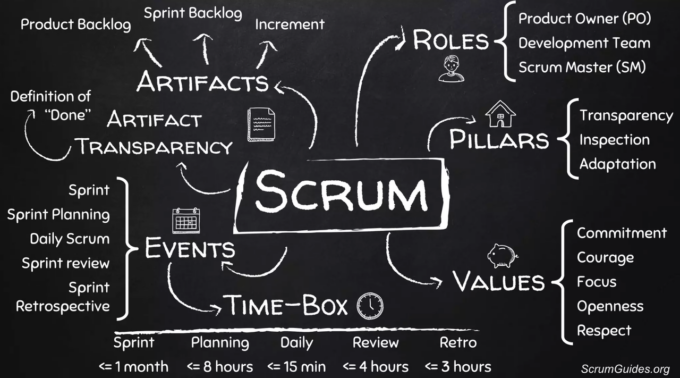
Scrum is guided by a set of principles and values, including transparency, inspection, and adaptation.
It is based on empirical process control, which means that decisions are made based on observed outcomes rather than predictions.
Scrum is known for its flexibility and ability to adapt to changing requirements and priorities, making it suitable for complex and dynamic projects. It promotes collaboration, transparency, and a focus on delivering value to the customer in short, iterative cycles. It has become popular in a wide range of industries beyond software development and is used for various types of projects.
Who is a Scrum Master?
A Scrum Master is a key role within the Scrum framework, which is an agile methodology used for managing and delivering software projects. The Scrum Master’s primary responsibility is to facilitate and support the Scrum team in adhering to Scrum principles and practices.
Qualities of a Certified Scrum Master
The role of a Certified Scrum Master (CSM) is crucial in Agile project management. It involves coordinating teams, simplifying work processes, and guiding the implementation of Scrum, an Agile methodology. This essay highlights the top 10 qualities a CSM should possess to excel in their role.
1. Leadership

One fundamental quality a CSM must showcase is leadership. The CSM is expected to lead by example, providing guidance and mentoring their team. Their leadership style is servant leadership, where the focus is on the needs of the team members, encouraging and helping them achieve their tasks instead of commanding.
2. Communication

Effective communication is vital in Scrum methodology. A Certified Scrum Master should be able to clearly articulate the vision, goals, and tasks. They should also be a good listener, being receptive to team members’ ideas, concerns, and suggestions.
3. Problem-Solving
A CSM must demonstrate strong problem-solving skills. Obstacles are common in project implementation; having the ability to quickly identify and resolve these issues will streamline processes and boost productivity.
4. Flexibility
The Agile methodology thrives on change and adaptation. As such, a CSM should be flexible enough to adjust to changes in plans, technologies, and strategies without affecting the overall project outcomes.
5. Knowledge of Scrum Practices
An extensive understanding and grasp of Scrum principles, practices, and tools are required of a CSM. This knowledge aids in interpreting the rules of Scrum to the team accurately and implementing them effectively.
6. Commitment
A CSM’s dedication to their role, team, and project is another integral quality. This commitment reflects in their perseverance to face challenges and their readiness to allocate extra time and effort when required, to ensure success.
7. Teamwork

A CSM isn’t just a leader; they’re an integral part of the team. They should promote and excel in teamwork, fostering an environment of collaboration, and shared responsibility. They act as a bridge between the team and the organization, ensuring that all parties work together efficiently.
8. Ability to Teach and Mentor
The CSM should create a learning environment that encourages team growth. The ability to teach and mentor team members about Scrum practices and principles sets a foundation for continuous learning and individual development.
9. Conflict Resolution
In team settings, conflicts are inevitable. A CSM should exhibit strong conflict resolution skills. They should neutralize tension within the team and address conflicts in a professional and unbiased manner.
10. Negotiation Skills
Negotiation skills are essential in managing the often dynamic and challenging stakeholder expectations. A CSM should be equipped to mediate between various parties and negotiate a middle ground when interests vary, ensuring everyone’s needs are met without compromising the project’s success.
Conclusion
Being a Certified Scrum Master is not just about certification. You invest time and hardwork in preparing for the CSM Exam. It entails a blend of soft skills, technical expertise, and dedication to Agile principles. A CSM possessing these top 10 qualities – leadership, communication, problem-solving, flexibility, knowledge of Scrum practices, commitment, teamwork, ability to teach and mentor, conflict resolution, and negotiation skills – will undoubtedly manage Scrum teams to achieve stellar results and significantly contribute to success in an Agile environment.










