3D printing has hit mainstream manufacturing. However, it hasn’t made conventional manufacturing methods like injection molding or CNC machining obsolete. Each manufacturing method has its pros and cons. However, CNC machining and 3D printing are both frequently chosen for the same production jobs. So, what is the better option between 3D printing and CNC machining for your operation? Let’s learn more about each manufacturing technology before we outline when one or the other is best for your application.
What is 3D printing?
3D printing is always classified as additive manufacturing. You start from scratch and print or extrude material to build a three-dimensional item layer by layer. The original 3D printers only worked with a plastic polymer. More advanced and expensive 3D printers can work with metal and other materials. 3D printing may deliver a final product for you to use, or it may require some post-processing like grinding or sanding.
What is CNC Machining?
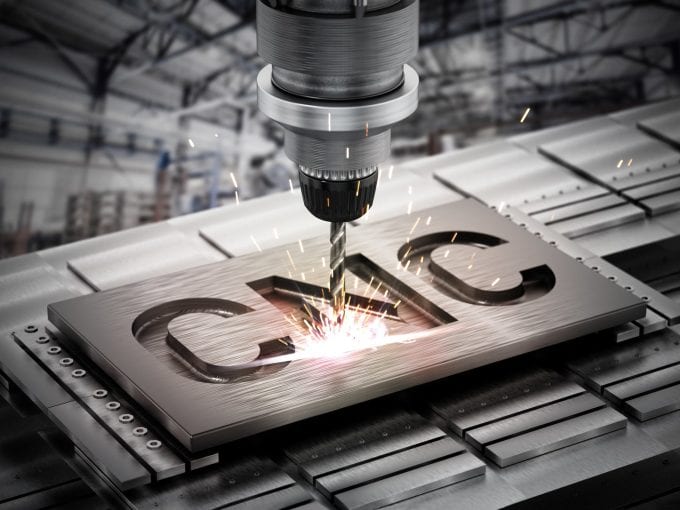

The CNC in machining stands for computer numerically controlled. A CNC machine contains several different machining tools, each controlled by an advanced, specialized server. It can cut, drill, and otherwise manipulate a block of material based on the instructions it has been given. It doesn’t need an operator except to put the material in and take it out, though a robot arm may do that. The models used by CNC milling machines are created using 3D modeling software like that used to create instructions for 3D printers.
The Benefits of CNC Machining

- CNC machines can work with almost any material. They can process metal alloys, softwoods, hardwoods, acrylic, foam, plastic, and machining wax. The CNC machining of wax gives you the positive model required for casting. It also means that the final item coming out of the CNC machine is made from the same material as the final product. That allows you to start accurate product testing almost immediately.
- CNC machines are designed to let you swap out tools quickly. This means you can promptly switch materials or operations. Then load the right instructions, add the next block of material, and go.
- They offer, on average, far tighter tolerances. It is not uncommon for them to have positioning accuracies of 0.001 inches or 0.025 millimeters. And their manufacturing tolerances are 0.005 inches. It is rare for a 3D printer to approach these tolerances, and that is aside from the risk that 3D printers may deform the material after it has been extruded.
- They are faster on a per-item basis. With a piece of the same complexity and size, the CNC machine will finish it in less than an hour, whereas the 3D printer takes several hours. Work with services that have a large number of machines, and they can turn out a large number of finished items each shift. This rivals the production rate of other mass production systems.
The Downsides of CNC Machining

CNC machining cannot create voids inside the structure that dramatically reduce its weight. It can, at best, drill holes or cut out large sections of the material.
These machines cut and chip away at the solid block or semi-finished piece it is given. This creates a safety hazard. That’s why are often enclosed and must be closed while operating. In contrast, many 3D printers are safe enough to sit on a desk and run. Just don’t touch the hot base or the molten plastic.
The Benefits of 3D Printing

- 3D printing allows you to create intricate reinforced designs with a minimum of material. This often results in lighter assembled structures.
- 3D printing is capable of complex design geometries you cannot get with traditional machining methods. You might get the same shapes with manual processing, but now you’re introducing high labor costs and more significant variation into the process.
- CNC machines require setup to be able to process the material. This may range from seconds to hours. 3D printers can start printing as soon as they have the print instructions and the material. If you switch designs, the 3D printer doesn’t require anything new unless you’re switching resin. This is why 3D printers are better for small production lots and unique items.
- 3D printing is ideal when you’re doing prototype molding. It can give you a single physical model of the product that you can show to clients or potential customers. This is invaluable whether you’re raising money to pay for mass production or trying to land your first contract.
- 3D printing can create the mold you want to be used by injection molding services. However, this is only possible if you’re using a resin that has a high-temperature resistance. Yet you can use the 3D printed part to show injection molders what you want the final product to look like so that they come up with the best possible mold for mass production.
The Downsides of 3D Printing

You can’t 3D print in wood or foam; 3D printing is limited to a few resins and thermoplastics. And, 3D printers may be able to handle only resin or thermoplastics, not both. This limits what you can print and which printer you can use to print it.
3D printing isn’t as accurate as the average CNC machine can deliver. And the 3D printers that offer nearly equal tight tolerances and print accuracy tend to go far slower than either CNC machines or the typical 3D printer.
Most 3D printers can’t print anything more substantial than a coffee can. Some of the largest production 3D printers have a build volume of 36 inches by 26 inches by 36 inches. For comparison, the biggest CNC machines have cut envelopes of 84 inches by 40 inches by 36 inches. And that is aside from the fact that they can build a part by splitting it into pieces, making each, and then assembling or welding it together.
When 3D Printing is Best

If you’re making one unique item or several variations of the same design, 3D printing is the better choice. However, it is possible to essentially mass-produce 3D printed items as well as CNC machined items. For example, services like RapidDirect can take your design and run it through their vast bank of 3D printers. They have a massive facility capable of making thousands of parts a day. This makes them unusual among rapid prototyping services. And they can make other items via sheet metal fabrication, too.
The sheer number of machines they have means they could create and ship back 50 different versions of your prototype for testing, or make your first 500 production parts far faster than you could set up and run a small bank of CNC machines. The firm offers you the chance to pass over your CAD or 2D drawing, then provide specifications such as size and material preference, then wait for the finished product to arrive. This quick and easy solution is perfect for busy companies that need swift, quality products. If you want to learn more about RapidDirect and what they have to offer, you can find out more information here.
When CNC Machining is Best
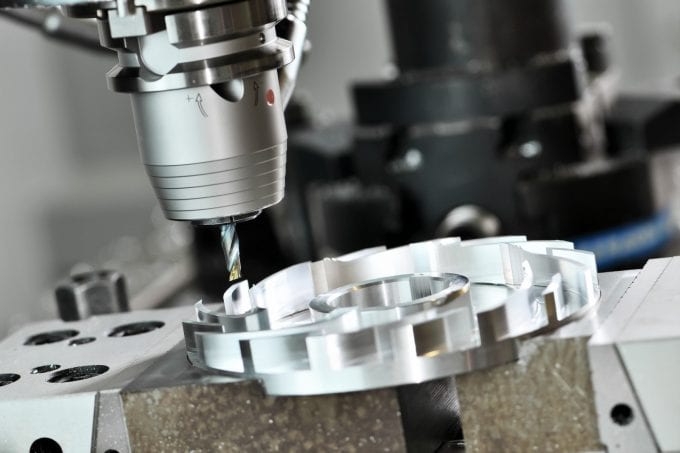

If you’re going to make small to moderately large lots such as your first 100 parts, CNC machining is generally better because it is faster and cost-effective at that scale.
CNC machining is also best for producing mid-size to full-size production runs. Even with a bank of 3D printers, CNC machines will outpace printers every time. According to Fictiv, CNC machining is a fast, valuable, and ideal subtractive manufacturing resource for all metal parts, small parts with a tight radius, and parts that require the smallest margin of error possible. Due to the CNC machine’s ability to create parts that meet precise requirements, entire industries, including aerospace, automotive, and the medical field, rely on CNC machining to create parts for everything from space shuttles and cars to surgical equipment used in the operating room.
CNC machining can also be used to create large volumes of items that are used in other consumer industries, like bicycle parts, engraved home décor, and even keychains. While CNC machine shops aren’t likely to produce home décor items in large quantities, the ability to do so shows that the diversity of CNC machines is unparalleled. A machine shop can produce a far wider selection of items than a 3D printer can at this point. While that may change in the future, CNC machining is the clear winner when it comes to the diversity of materials and items they can handle.
This servicing is a critical aspect of maintaining optimal manufacturing operations.
Regular servicing ensures that Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines, which play a pivotal role in modern industrial processes, remain efficient and accurate.
Trained technicians perform tasks like lubrication, calibration, and inspection of components to prevent wear and tear. By addressing potential issues proactively, CNC machine servicing minimizes downtime, reduces the risk of breakdowns, and extends the machine’s lifespan.
This contributes to consistent product quality, improved productivity, and cost-effective production processes, making CNC machine servicing an indispensable practice in the manufacturing landscape
CNC machining is the only choice if you’re working with materials that cannot be 3D printed. And CNC machining is the best choice if you’re dealing with huge items.
While the performance gap between 3D printers and CNC machines narrows, there are material and size restrictions that will prevent 3D printing from making CNC machining obsolete. Consider them complementary technologies, and choose the right one for your manufacturing job.









