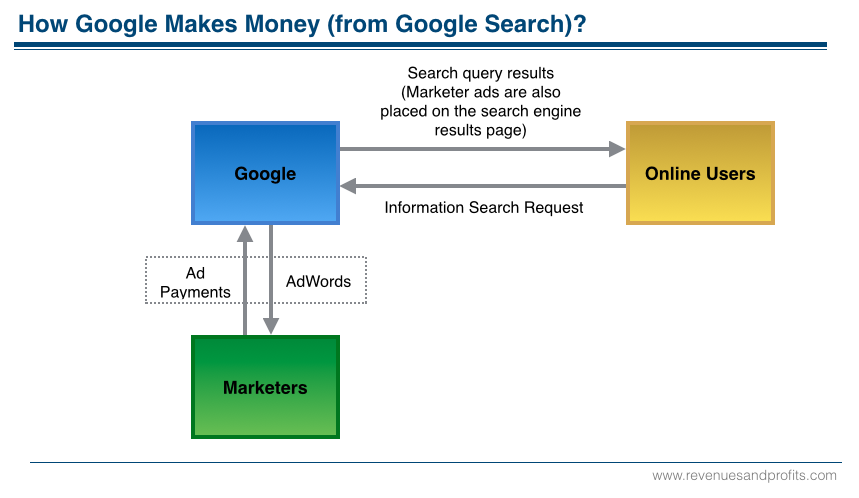
This post is about how Google makes money. Firstly, we explain Google offerings for the online users, the advertisers, and the enterprises. Then, we provide Google product segment revenues for the years 2010 to 2014. Then, we share the information on Google cost elements, profits, and profit margins.
Google is a global technology leader focused on improving the ways people connect with information. Google offer its products for free to the online users. Google enables marketers target the online users with its advertising products. Google generates revenue primarily by selling online advertising over its sites and its network member sites.
Google Network is the network of third parties that use Google advertising programs to deliver relevant ads over their sites. Google generates a small percentage of revenue from its enterprise products, consumer content platforms, commerce, and hardware products.
Google Offerings For Online Users
For the online users, Google offers a range of products for web search, email, content creation, content storage, content publishing and sharing, commerce, and hardware. Here are some of the Google products that are popular among the online users:

- Google Web Search. It helps people find what they are looking for on the web. Users can access it by visiting google.com. Google also offers products such as Google News, Google Finance, Google Maps, Google Image Search, Google Book Search, Google Scholar, and Google Groups that let its users search news, business financials and stocks information, maps, images, books, scholarly literature, and groups Information respectively.
- Gmail. It is a free web mail service that allow users to send and receive emails. There is an instant messaging system integrated in Gmail as well.
- Google Docs. It allows users to create, view, and edit documents, spreadsheets, and presentations using a browser. The documents are stored on Google servers and allow real-time editing with other users over the Internet.
- Chrome browser. It is a web browser that lets users surf the web.
- Android operating system for smartphones. It is a free, fully open source mobile software platform that any developer can use to create applications for mobile devices and any handset manufacturer can install on a device.
- Google Play. It is a cloud based digital entertainment store for apps, books, music, and movies.
- Google+. It is a social networking site
- Youtube. It is a video sharing site that Google acquired in November 2006.
- Blogger. It is a web-based publishing tool for publishing of blogs.
- Google Wallet. It is a virtual wallet that securely stores users’ credit and debit cards, offers, and rewards cards.
- Consumer hardware products. These include Chrome OS notebooks, Nexus smartphones and tablets, and Chromecast.
Google Offerings For Advertisers
Google offers following products to the advertisers:
- Google AdWords. It is an auction-based advertising program that delivers ads based on user search queries. Advertisers bid on the keywords that will trigger display of their ads. Advertisers can display their ads over Google sites or Google Network websites. Google receives money from the advertisers when online users click those ads.
- Google AdSense. It helps content owners monetize their content. It enables Google Network member web sites to deliver AdWords ads that are relevant to the search results or content on their pages. Google shares most of the revenue generated from ads shown by the network member with that member.
- DoubleClick Ad Exchange. It is a real-time auction marketplace for the trading of display ad space.
Google Offerings For Enterprises
Google offers the following enterprise products to its enterprise customers:
- Google apps for business. It includes Gmail, Google Drive, Calendar, Google Sites, and more.
- Google Maps Application Programming Interface (API) for businesses. It includes fully interactive Google Maps for public and internal websites.
- Google Earth Enterprise. It is a behind the company firewall software solution for imagery and data visualization.
- Google Cloud Platform. It is a suite of infrastructure and cloud services for developers and businesses. This includes
- Platform as a Service (PAAS) offering called Google App Engine
- Storage through Google Cloud Storage
- Real time analytics through Google BigQuery
- Structured Query Language (SQL) through Google Cloud SQL
- Infrastructure as a Service (IAAS) via Google Compute Engine
Visit Emit.reviews to see other cloud hosting service providers that use similar methods to make money. Nowadays, cloud technology has become quite popular & is used almost in all online companies.
Also, check out this rank and rent guide from DiggityMarketing on how you can make money from your existing site.
Google Revenues 2014

In 2014, Google generated $66 billion of total revenues. Of these total revenues, Google generated
- $45 billion revenues, 68.3% of the total, from the advertising over the Google websites. Revenues from Google websites include revenues generated from ads served on Google owned and operated properties such as Google Search, Youtube, Google Maps, and Google Finance.
- $14 billion revenues, 21.2% of the total, from advertising over the Google Network Member’ websites. The share of Google Network Member’ websites revenue declined from 30% in 2010 to 21.2% in 2014. Revenues from Google Network Members’ websites include revenues from ads served through advertising programs such as AdSense for search, AdSense for content, AdExchange, AdMob, and DoubleClick Bid Manager.
- $7 billion revenues, 10.5% of the total, from other sources. The share of other revenues increased from 3.7% in 2010 to 10.5% in 2014. Google generates other revenues primarily from sales of: digital content products such as apps, music, and movies over the Google play store; hardware sales of products such as Chromecast, Nexus smartphones and tablets, and Chrome OS notebooks; and Google enterprise products.
Google Profits 2014
Of the $66 billion of Google total revenues in 2014, $25.7 billion were the cost of revenue. This resulted in $40.3 billion of gross profit and a gross margin of 61.1%. Google spent $9.8 billion, $8.1 billion, and $5.6 billion on research and development, marketing and sales, and general and administrative expenses respectively.
This resulted in $16.5 billion of operating profit and an operating margin of 25.0%. After interest and other income/expenses and income taxes, Google had a net profit of $14.4 billion and a net margin of 21.9%.

Here are the definitions of Google’s key costs and operating expenses:
- Cost of revenue. This includes traffic acquisition costs and other cost of revenue. Traffic acquisition costs consists of the advertising revenue that Google shares with its network members and the amounts that Google pays to its distribution partners who distribute Chrome browser or otherwise direct search queries to Google website. Other cost of revenue includes: (a) content acquisition costs, primarily related to payments to certain content providers who license their content for distribution on Youtube and Google Play; (b) the expenses related to data center operations (including depreciation, labor, energy, and bandwidth costs); (c) Inventory costs of the hardware Google sells; (d) Credit card and other transaction fees related to processing the customer transactions; (e) amortization of intangible assets.
- Research and development. These expenses consist primarily of: (a) Labor and facility-related costs for employees responsible for R&D in existing businesses as well as new products and services; (b) Depreciation and equipment related expenses; (c) Stock-based compensation expense for employees responsible for R&D.
- Marketing and sales. These expenses consist primarily of: (a) Labor and facility-related costs of personnel engaged in sales and marketing, sales support, and certain customer service functions; (b) Advertising and promotional expenditures related to Google’s products and services; (c) Stock-based compensation expense for employees engaged in sales, sales support, and certain customer service functions.
- General and administrative. These expenses consist primarily of: (a) Labor and facility-related costs for personnel in Google facilities, finance, human resources, information technology, and legal organizations; (b) Professional services fees primarily related to outside legal, audit, information technology consulting, and outsourcing services; (c) Amortization of certain intangible assets; (d) Stock-based compensation expense.